Introduction
Pathology is undergoing a seismic shift, moving away from the traditional methods that have been standard for over a century. Histopathology, which traditionally relied on thinly sliced tissue sections mounted on glass slides, is evolving with advancements in slide-free optical microscopy. This novel approach eliminates many bottlenecks associated with conventional workflows, such as time-consuming sample preparation and staining processes. By imaging intact tissue samples directly, slide-free techniques enable faster diagnostics, better data fidelity, and broader access to pathology services, especially in remote or resource-limited areas. To help you learn more about these cutting-edge advancements in slide-free technology, this post is sponsored by Muse Microscopy.
Introducing Slide-Free Pathology
Among the various emerging technologies in slide-free pathology, the MUSE (Microscopy with UV Light Surface Excitation) system stands out as the first mature solution. MUSE offers a novel direct-to-digital workflow that bypasses the traditional reliance on glass slides and manual staining. In this article, we’ll explore MUSE’s workings, advantages, and potential to change the pathology workflow as we know it.
What is Direct-to-Digital Pathology?
Direct-to-digital pathology replaces and/or complements the conventional histopathology workflow by capturing diagnostic quality images of fresh or minimally processed tissues directly from the sample. Unlike traditional processes that rely on embedding tissues in paraffin, slicing them into thin sections, and staining them on glass slides, this innovative approach employs advanced optical and computational methods to analyze intact specimens.
Direct-to-Digital Advantages include:
- Faster Turnaround: By eliminating steps like microtome slicing and staining, results can be delivered in minutes.
- Non-Destructive Imaging: Tissue remains intact, preserving it for further analysis if needed.
- Accessibility: Digital images can be shared instantly, facilitating remote consultations.
Understanding the MUSE Technology
The MUSE system is a pioneering tool in the slide-free pathology space. By using UV light surface excitation, it produces high-resolution fluorescent images of tissues without requiring traditional glass slides or chemical staining.
Core Features of MUSE:
- UV Surface Excitation: Uses short-wavelength UV light to excite tissue, generating autofluorescent signals that can be captured digitally.
- Integrated Workflow: Tissue samples are placed in a cassette, imaged directly, and digitally converted into an H&E-equivalent format.
- Compact Design: The system’s small footprint allows deployment in labs, clinics, or other near patient settings.
MUSE creates images in just 2 to 15 minutes, depending on the size and complexity of the tissue sample.
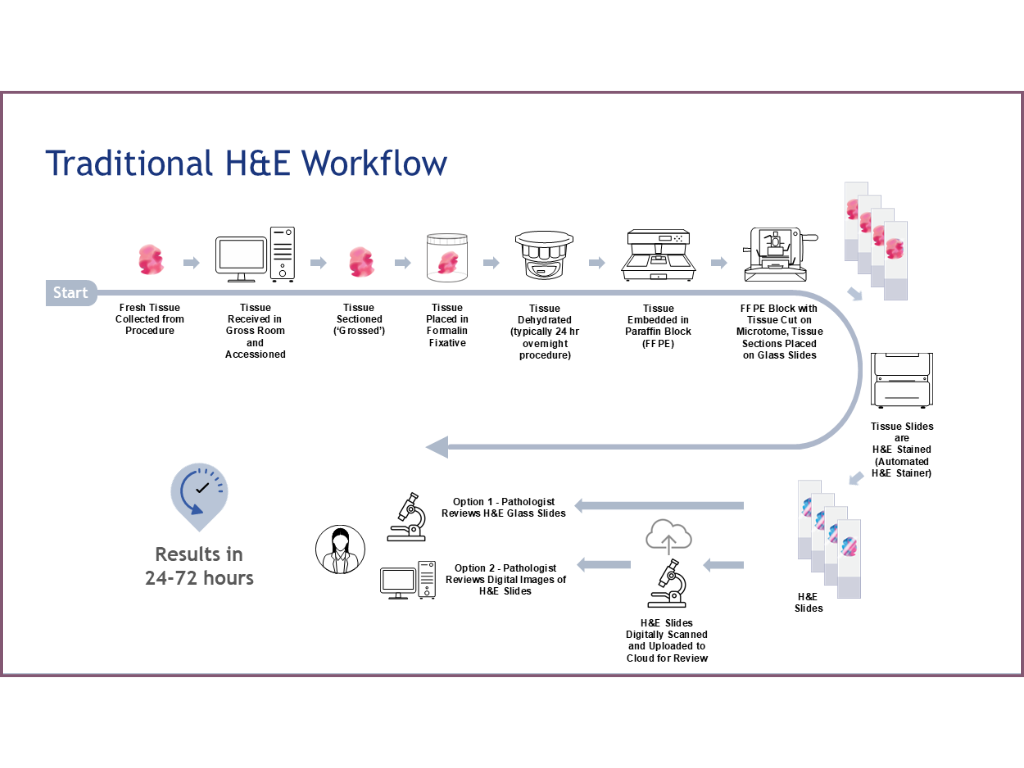
The Digital Pathology Workflow with MUSE Technology
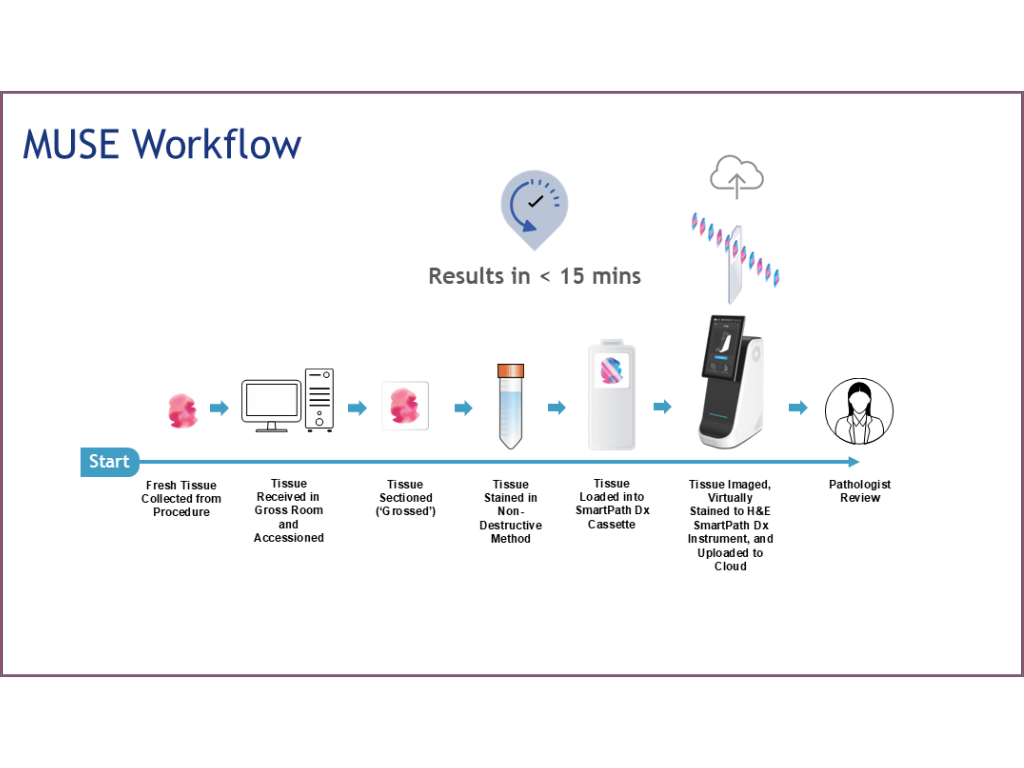
Sample Preparation Phase
- Tissue Collection: Fresh tissue is collected from the procedure and transferred to the gross room for initial processing.
- Initial Processing: The tissue is received, accessioned, and prepared in the gross room according to standard protocols.
- Tissue Sectioning: The specimen is sectioned (“grossed”) to appropriate specifications.
- Non-Destructive Staining: The tissue undergoes a non-destructive dying method, preserving the sample integrity with superior RNA retention to traditional FFPE.
Digital Imaging Phase
- Sample Loading: The tissue is loaded into a SmartPath Dx cassette and instrument for processing.
- Macro Imaging: A secondary camera captures a macro tissue image and records tissue coordinates and sample identification information.
- Region Selection: Through the user interface (UI), technicians review the macro tissue image and select the whole slide imaging (WSI) or regions of interest (ROI).
- High-Resolution Imaging:
- Utilizes a primary camera with a 10X objective under UV LED illumination
- Features autofocus capability
Image Processing Phase
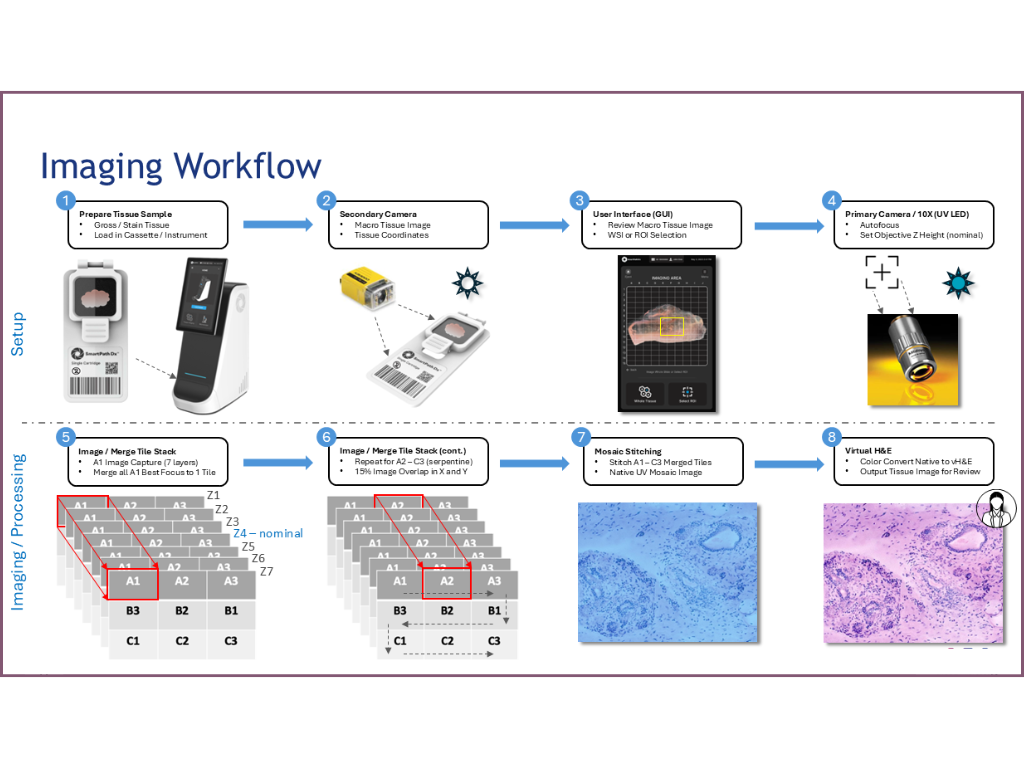
- Multi-Layer Capture:
- AI-driven image capture of 7 distinct layers
- Merges all A1 best focus to a single merged tile
- Tile Processing:
- Repeats process for A2-C3 (serpentine)
- Maintains slight image overlap in the X and Y axis
- Mosaic Generation:
- Stitches A1-C3 merged tiles
- Creates native UV mosaic image
- Virtual H&E Conversion:
- Converts native UV mosaic image to virtual H&E format
- Produces final tissue image for pathologist review
Review Phase
- Images are typically available within 30 minutes of initial processing.
- Images are automatically uploaded to cloud storage or the lab LIS system
- Pathologists can perform online reviews of the digitized images
Elimination of Glass Slides: A Game-Changer
Traditional histopathology relies heavily on glass slides, which are prone to breakage, mislabeling, and degradation over time. MUSE removes this dependency, offering a glass-free, slide-free approach that retains all the diagnostic details while minimizing logistical challenges.
Key Benefits:
- Durability: Eliminates the risk of physical damage to specimens during handling or transport.
- Cost Savings: Reduces material and labor costs associated with slide preparation.
- Improved Image Quality: Avoids artifacts commonly introduced during slicing and staining.
Speed and Efficiency for Diagnostics
In healthcare, time is critical, especially for diagnosing life-threatening conditions such as cancer. Traditional pathology workflows often take days to weeks, but MUSE accelerates this process to deliver actionable insights within minutes.
For example, during a breast biopsy, MUSE can provide preliminary information in a near-patient setting, assisting with fast treatment decisions. This is a stark contrast to the current workflow, where patients may wait days or weeks for results.
Advanced Imaging Capabilities
One of the standout features of MUSE is its ability to provide deeper tissue imaging giving potential to 3D imaging. By stacking multiple Z-layers, the system produces topographical images that offer depth and detail far exceeding traditional methods.
Imaging Depth:
- MUSE: Penetrates up to 50 microns into tissue.
- Traditional Glass Slides: Limited to 5 microns, offering only a 2D perspective.
This capability is invaluable for applications like stereology, where understanding the 3D structure of tissue is crucial for scientific studies or drug development.
Fluorescence and Virtual Staining
MUSE employs UV excitation to generate fluorescent images, which are then digitally converted into an H&E-equivalent format. This virtual staining process eliminates the need for chemical dyes, offering a safer and more sustainable alternative.
How it Works:
- UV Light: Excites tissue to produce natural fluorescence.
- Digital Processing: Converts fluorescence into diagnostic quality H&E-like images.
- Optional Dyes: For enhanced imaging, non-toxic dyes like DAPI can be used.
This approach ensures consistent and reproducible results, making it ideal for both clinical and research applications.
Applications of MUSE in Pathology
Human Medicine:
-
- Rapid Diagnostic Quality Images: Ideal for intraoperative consultations, where surgeons need immediate feedback.
- Remote Pathology: Enables specialists to analyze images from distant locations, improving accessibility in underserved areas.
- Cancer Detection: Provides precise imaging for evaluating tumor margins and cellular abnormalities.
Veterinary Medicine:
The portability and ease of use make MUSE a perfect fit for veterinary clinics and mobile units. Pathologists can quickly diagnose conditions in animals, from biopsies to organ evaluations, without the need for specialized lab infrastructure.
Implications for Remote and Resource-Limited Areas
In regions lacking histology labs or trained pathologists, MUSE could revolutionize access to pathology expertise by providing a self-contained solution for tissue analysis. Equipped with Wi-Fi or cellular connectivity, the device can transmit images to specialists anywhere in the world, enabling real-time consultations.
Additionally, its portability opens possibilities for deployment in field hospitals, community near-patient settings, and even disaster zones, where traditional pathology resources are unavailable.
Challenges and Misconceptions
Despite its advantages, transitioning to a slide-free workflow may face initial resistance due to:
- Adoption Barriers: Medical professionals accustomed to traditional methods may need time to adapt.
- Training Requirements: While SmartPath MUSE Technology™ (SmartPath) is user-friendly and less complex than preparing FFPE tissue and glass slides, training is necessary for optimal use.
- Regulatory Hurdles: FDA approvals and reimbursement models as well as new clinical protocols need to evolve to accommodate these technologies.
Addressing these challenges will require collaboration between manufacturers, clinicians, and regulatory bodies.
Reimbursement and Cost-Effectiveness
MUSE could potentially leverage existing CPT codes for pathology evaluation an apply for new codes if necessary, simplifying its adoption in clinical settings. By reducing labor and material costs while improving efficiency, it offers a financially compelling alternative to traditional workflows.
The Future of Pathology: A Digital Vision
MUSE represents just the beginning of a broader shift towards digitization in pathology. As these technologies become more widespread, we can anticipate:
- Increased Use of AI: Automated tools to assist in diagnosis and image analysis.
- Broader Accessibility: Deployment in underserved and remote regions.
- Enhanced Patient Outcomes: Faster decisions based on the diagnostic quality images leading to timely treatment.
As Matthew Nunez, CEO of MUSE, aptly said, “The future is here.” This technology has the potential to redefine how pathology is practiced, bringing it closer to the patient and enabling faster, more effective care.
FAQs
1. What is MUSE?
MUSE is a slide-free tissue imaging device for pathology that uses UV light excitation to generate digital images of tissue samples without the need for glass slides.
2. How fast is MUSE?
The system creates images within 2 to 15 minutes, depending on the sample size.
3. Can MUSE replace traditional pathology methods?
While it complements existing workflows, MUSE is particularly valuable for rapid image acquisition and non-destructive analysis.
4. Is MUSE suitable for veterinary medicine?
Yes, its portability and ease of use make it ideal for veterinary applications.
5. What are the cost implications of adopting MUSE?
MUSE reduces overall costs by eliminating slide preparation and associated logistics with the potential of leveraging existing reimbursement codes.
6. What is the imaging depth of MUSE?
MUSE can image up to 50 microns, offering a 3D perspective that traditional slides cannot.
Conclusion
The MUSE system is a transformative innovation, pushing the boundaries of pathology and redefining diagnostic workflows. By eliminating traditional bottlenecks, it paves the way for faster, more efficient, and more accessible pathology services across the globe.
Related Contents
- https://youtu.be/Iu44e68fPYo?si=kzwljkEcWNcur-Zj
- https://youtu.be/cAbvU_PP_Ps?si=kf2cgQ86g_jEgYcf
- https://youtu.be/up2xDCiDRTQ?si=WbDdmuRQAe-Wvavs












Comments are closed.